In light of the growing challenges posed by global pandemics, Pandemic Hospital Design, Healthcare Infrastructure has become a critical factor in ensuring the continuity of medical services and safeguarding lives. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed both strengths and weaknesses in healthcare infrastructure worldwide, prompting experts to reconsider architectural and engineering standards in hospital planning. This article explores the key lessons learned from COVID-19 and the subsequent practical recommendations, focusing on essential components that make pandemic hospital design an effective tool for future health crises.
The Importance of Pandemic-Focused Hospital Design
As the spread of novel diseases and mutating viruses intensifies, healthcare systems must integrate pandemic-specific design principles into their development and expansion plans. The hospital layout must offer enough flexibility to shift between routine operations and emergency response modes while ensuring the safety of patients and healthcare workers. Efficient separation of infection pathways and quick adaptation capabilities are crucial to minimizing response times during health emergencies.

Core Principles of Pandemic Hospital Design
These principles focus on building a medical infrastructure capable of responding rapidly to crises without compromising the efficiency of daily operations. Flexible design layouts and precise spatial zoning provide a solid foundation that ensures ease in managing patient flows and implementing isolation protocols and other safety and security measures during emergencies.
1) Engineering Flexibility and Functional Zoning
Flexible engineering allows hospital units and rooms to be rapidly reorganized based on emerging needs. Through modular surfaces and detachable walls, entire internal departments can be converted into intensive care or isolation wards within hours. Clear functional zoning helps reduce crowding and directs medical resources efficiently, avoiding the need for costly external expansions.
2) Airflow Control and Ventilation Systems
Controlling air movement and ventilation is a cornerstone of pandemic-ready hospital design. Negative pressure systems and HEPA filters are essential in limiting the spread of airborne pathogens. Increasing air exchange rates to over 12 cycles per hour in isolation rooms creates a safer and healthier environment for both patients and staff, minimizing cross-infection risks.
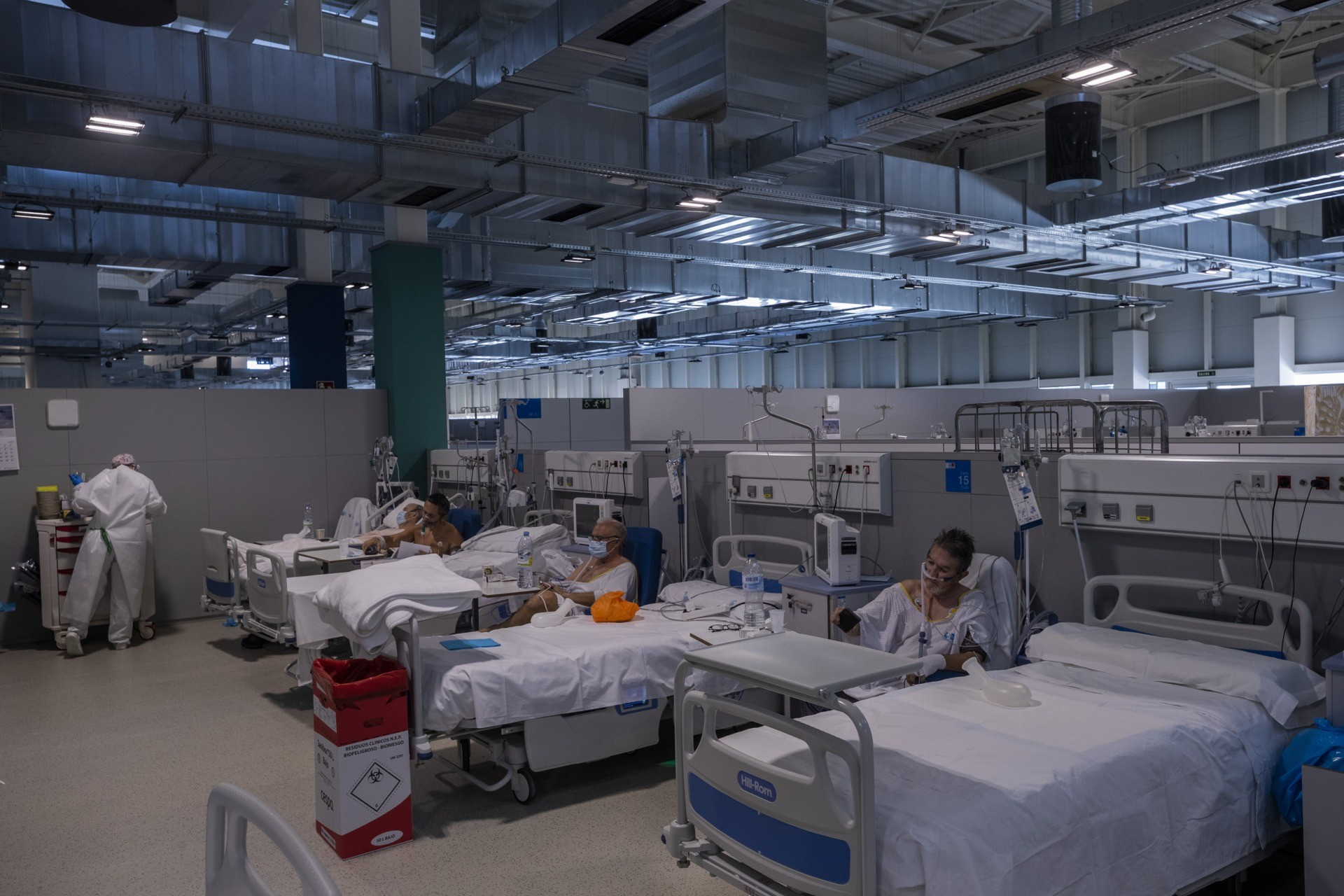
3) Dedicated Isolation Zones and Patient Pathways
Establishing dedicated pathways for patients suspected or confirmed to carry infectious diseases is vital. This includes primary screening entry points equipped with rapid diagnostic tools and temporary internal corridors with mobile barriers to house medical teams and disinfection units. These zones ensure complete separation between routine patient areas and those designated for pandemic cases.
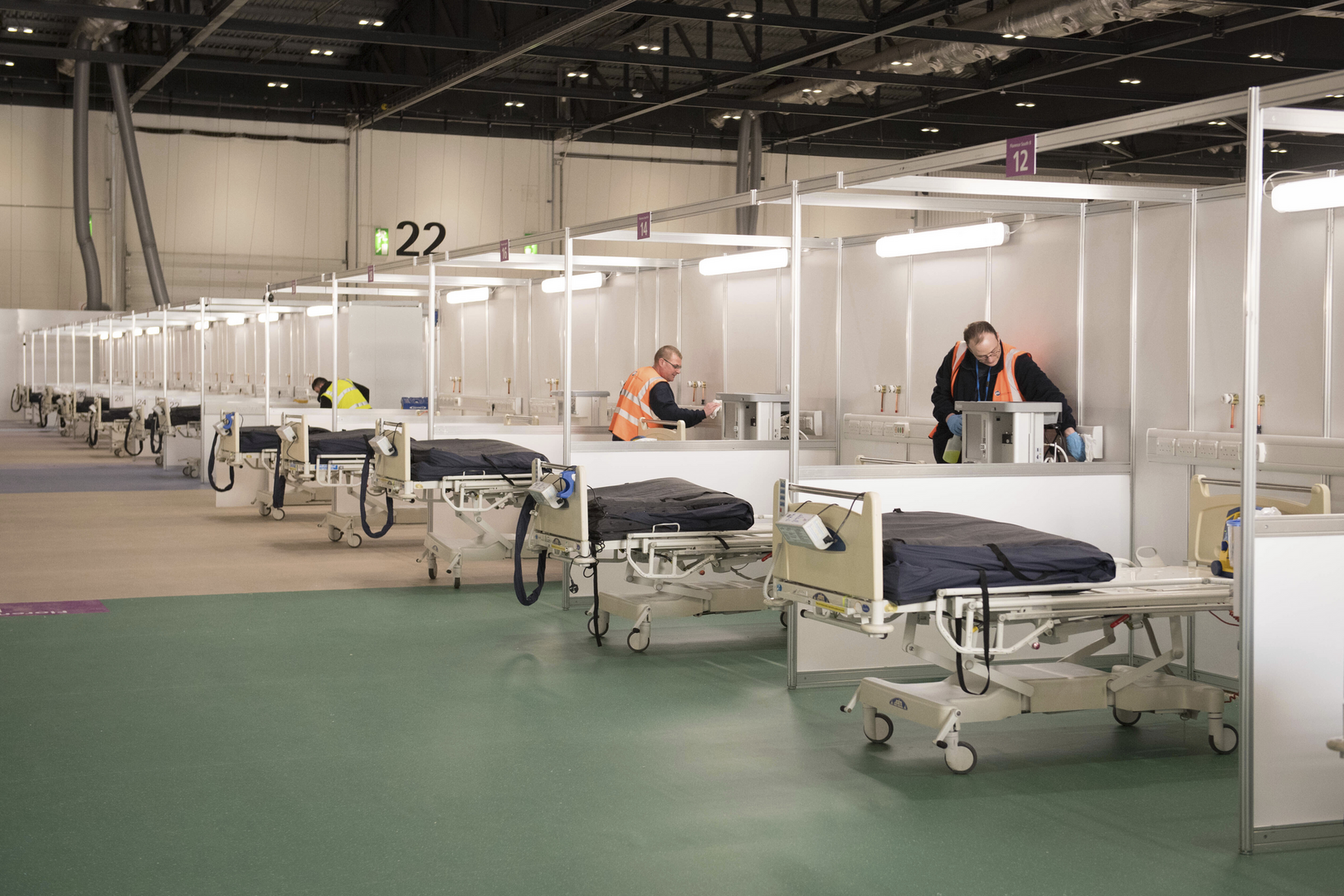
4) Architecture and Internal Circulation
Structured horizontal layouts and limited cross-traffic corridors help reduce contact points between patients and staff. A well-designed Pandemic Hospital Design, Healthcare Infrastructure plan includes distinct access points for staff, visitors, and logistics services. Emergency pathways allow critical cases to be transferred quickly without disrupting daily operations in other departments.
Get to know also: Your Guide to Medical Equipment Planning in Hospitals and Medical Centers
Key Lessons from COVID-19 in Pandemic Hospital Design
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a real-world stress test for hospital preparedness and response capabilities. It revealed critical insights into the weaknesses and strengths of healthcare systems worldwide. From this experience, experts developed a valuable set of lessons emphasizing the need for flexible and adaptive Pandemic Hospital Design, Healthcare Infrastructure to handle varying infection scenarios and emergency surges.
1) Cross-Functional Collaboration and Integrated Planning
COVID-19 demonstrated that collaboration between doctors, engineers, and administrative professionals is far more effective than siloed operations. Through interdisciplinary teams, some hospitals were able to build dedicated treatment wings within days instead of weeks. This rapid response helped alleviate pressure on intensive care units and improved overall patient outcomes during surges.
2) Embracing Digital Health and Telemedicine
Telemedicine platforms significantly reduced routine hospital visits while maintaining high-quality patient-doctor communication. As a result, integrating digital infrastructure such as high-resolution screens and secure network connections has become an essential component of Pandemic Hospital Design, Healthcare Infrastructure. These elements ensure continuity of care even when in-person services are limited.

3) Temporary Expansions and Operational Flexibility
At the pandemic’s peak, some hospitals resorted to setting up mobile units in parking lots or repurposing indoor halls as temporary emergency wards. This underscores the importance of flexible expansion strategies, including pre-planned lightweight structures and quickly deployable modular roofs. These solutions enable hospitals to accommodate patient overflow without disrupting essential services.
4) Maintaining Routine Services Alongside Emergency Response
It became clear that halting all routine medical services during a pandemic is not a viable option. One of the key takeaways was the necessity of dividing hospitals into distinct zones one for handling infectious cases and another for routine care. This zoning ensures that surgeries, critical diagnostics, and other vital procedures continue without delays or exposure risks.
Future Recommendations for Strengthening Pandemic Hospital Design
To ensure resilience and readiness, healthcare facilities must adopt innovative design strategies and operational frameworks that allow for adaptability, safety, and continuity of care.
- Modular Design for Rapid Expansion: Hospitals should adopt modular designs that allow for the quick addition or removal of treatment units as needed. This flexibility enables facilities to scale operations in response to evolving healthcare demands without requiring extensive structural changes.
- Advanced Ventilation Systems with Adjustable Pressure Control: Investing in dynamic ventilation systems is essential. These systems should have the ability to adjust air pressure levels based on the risk profile of each hospital zone, thereby minimizing airborne contamination and improving infection control.
- Smart Isolation Pathways and Electronic Zoning: The implementation of smart isolation corridors featuring electronic gates and mobile partitions ensures complete separation between infectious and non-infectious zones. These smart pathways optimize patient flow and enhance safety for both staff and patients.
- Digital Infrastructure to Support Telemedicine: Expanding digital infrastructure is vital for enabling telehealth services. Equipping hospitals with secure networks and high-tech communication tools allows remote management of infectious patients, reducing the need for direct contact while maintaining care standards.
- Pre-Arranged Contracts with Suppliers and Contractors: Establishing pre-crisis agreements with suppliers and construction firms ensures the swift delivery of essential materials and equipment during emergencies. This readiness significantly reduces response time and operational delays during outbreaks.
In conclusion, the deep challenges revealed by the COVID-19 pandemic underscore the necessity of embracing an advanced approach to Pandemic Hospital Design, Healthcare Infrastructure. At the forefront of this transformation is HSI Healthcare Systems International, a center dedicated to healthcare training and consulting, with a mission to elevate the biomedical engineering sector.
Under the guidance of top-tier experts, HSI offers more than just training. it delivers tailored consulting and professional mentorship to healthcare institutions aiming to enhance their technical and service infrastructure. Through this unique combination of education and strategic advisory, HSI provides a comprehensive platform that empowers professionals and organizations to take an active role in shaping a safer, smarter, and more innovative healthcare environment.
Source: Hospitals’ Collaborations Strengthen Pandemic Preparedness: Lessons Learnt from COVID-19