Radiology is a field that has revolutionized the way medical conditions are diagnosed and treated. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the fundamentals of Radiology 101, explore the various imaging methods, the science behind them, and their crucial role in modern healthcare. Whether you are a medical student, a patient seeking complete knowledge of radiology to feel reassured during imaging procedures, or simply someone interested in medical technology, this article will provide you with a solid foundation in medical imaging techniques.
Overview of Medical Imaging Techniques
Radiology 101 includes a wide range of medical imaging techniques essential for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. Understanding these techniques and their applications can help you appreciate the role of this type of rays in healthcare.
What is Radiology 101?
Radiology is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases within the human body. It involves the use of different imaging techniques to visualize the internal structures and functions of organs, tissues, and bones. This field has made tremendous progress over the years, enabling healthcare professionals to make more accurate diagnoses and develop precise treatment plans.
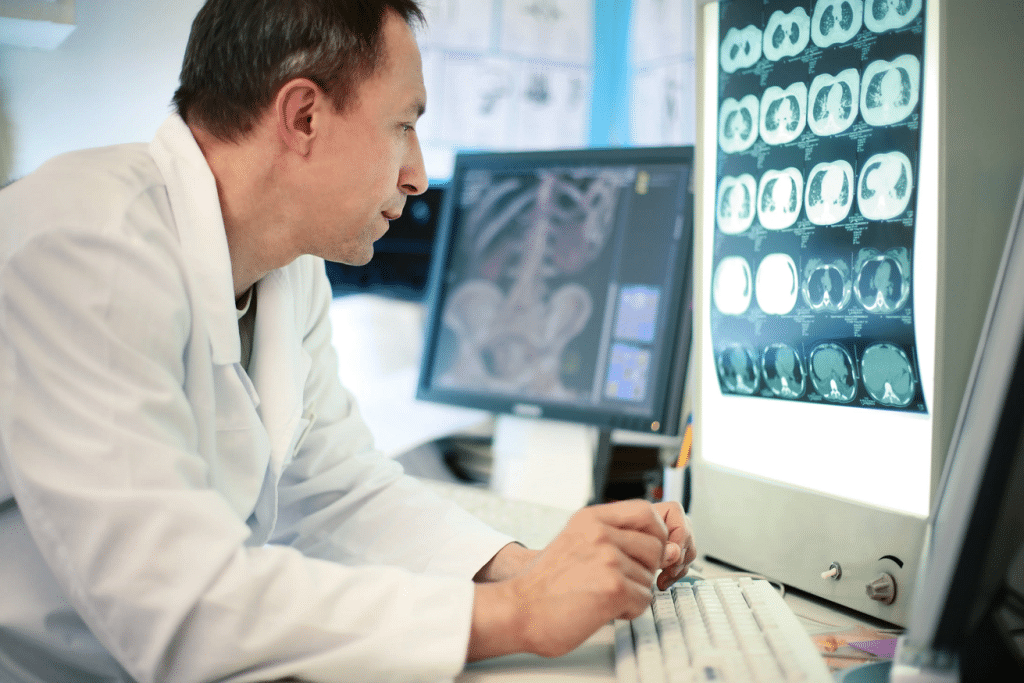
What are the Basic Principles of Radiology?
Radiology relies on the principles of ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, along with advanced computer technology. These principles have led to the development of various imaging techniques, each serving its purpose in diagnosing diseases. In the following sections, we will explore these imaging methods in more detail.
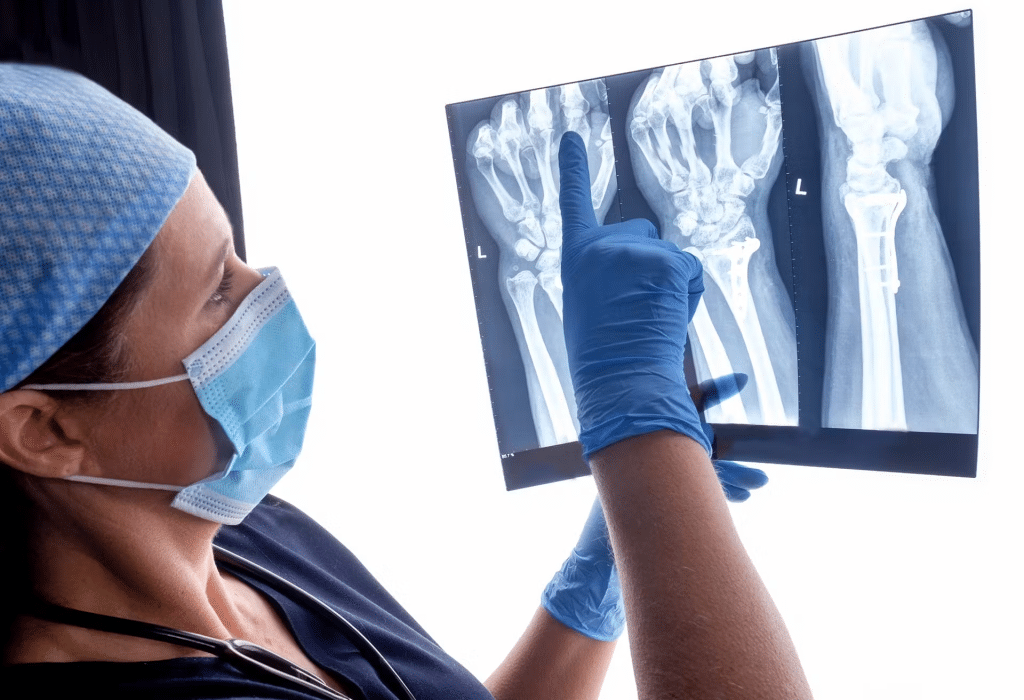
X-rays
X-ray imaging, also known as radiography, is one of the oldest and most widely used techniques in radiology. It involves using X-ray beams to create images of the inside of the body. X-rays are an essential tool for examining the skeleton, detecting fractures, and identifying abnormalities in the chest and abdomen.
How Do X-rays Work?
- Ionizing radiation is used to create images of bones and other dense structures.
- They are commonly used to detect fractures, infections, and lung diseases.
- When X-rays pass through the body, they are absorbed differently by various tissues.
- Dense tissues, such as bones, absorb more X-rays, which appears white on the X-ray film.
- On the other hand, soft tissues allow X-rays to pass through, making them appear darker on the film.
- This contrast helps radiologists determine the condition and make an accurate diagnosis.
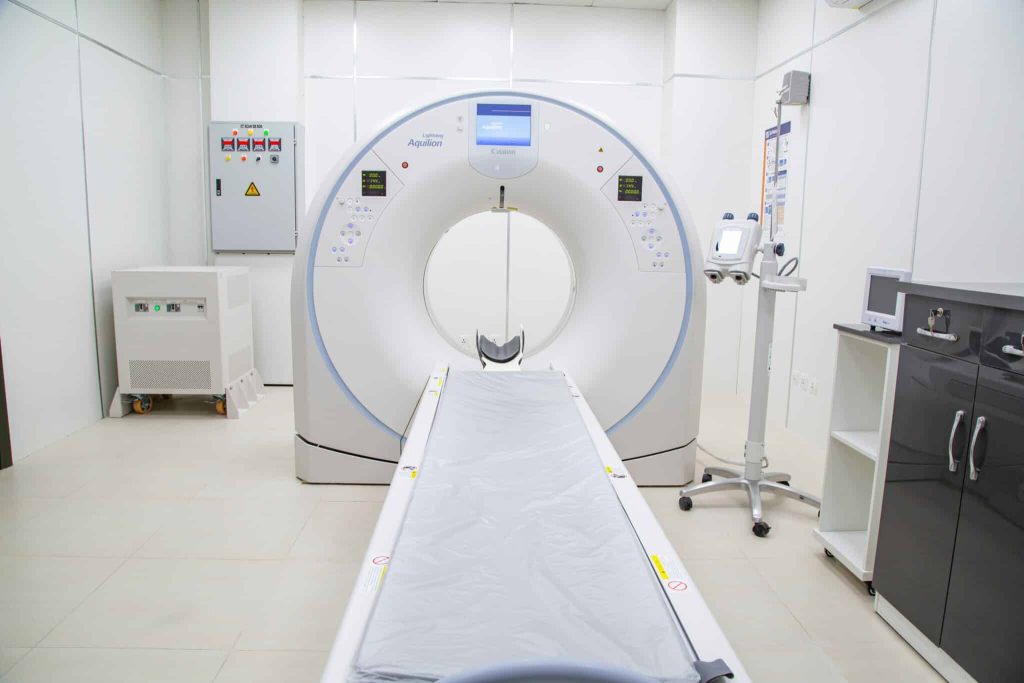
Computed Tomography (CT)
Computed Tomography (CT), often referred to as CT scanning or axial CT scanning, is a type of medical imaging technique that allows for detailed three-dimensional images of the body, providing valuable insights into both anatomy and pathology.
CT combines X-ray images taken from different angles to produce detailed cross-sectional images. It is particularly useful for diagnosing complex conditions such as head injuries, tumors, and internal bleeding.
How does CT produce a three-dimensional view?
- CT scanners work by capturing a series of X-ray images from different angles around the body.
- These images are then processed by a computer to create cross-sectional slices, similar to cutting a loaf of bread.
- The result is a three-dimensional representation of the scanned area, offering a more comprehensive view of the internal structures.
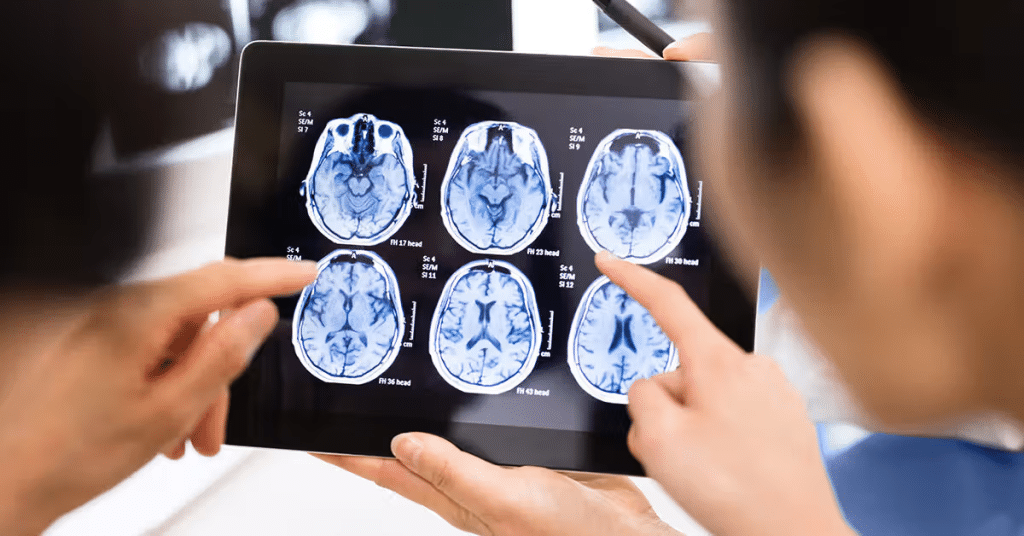
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides detailed images of soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, joints, muscles, and organs. Unlike X-rays and CT, which use ionizing radiation, MRI relies on magnetic fields and radio waves. Since MRI does not use radiation, it is considered a safer option for certain patients, including pregnant women and children.
How does MRI work without radiation?
MRI machines use powerful magnets to align hydrogen nuclei in the body. Then, radio waves are applied, causing these nuclei to emit signals. These signals are captured and converted into detailed images by a computer.
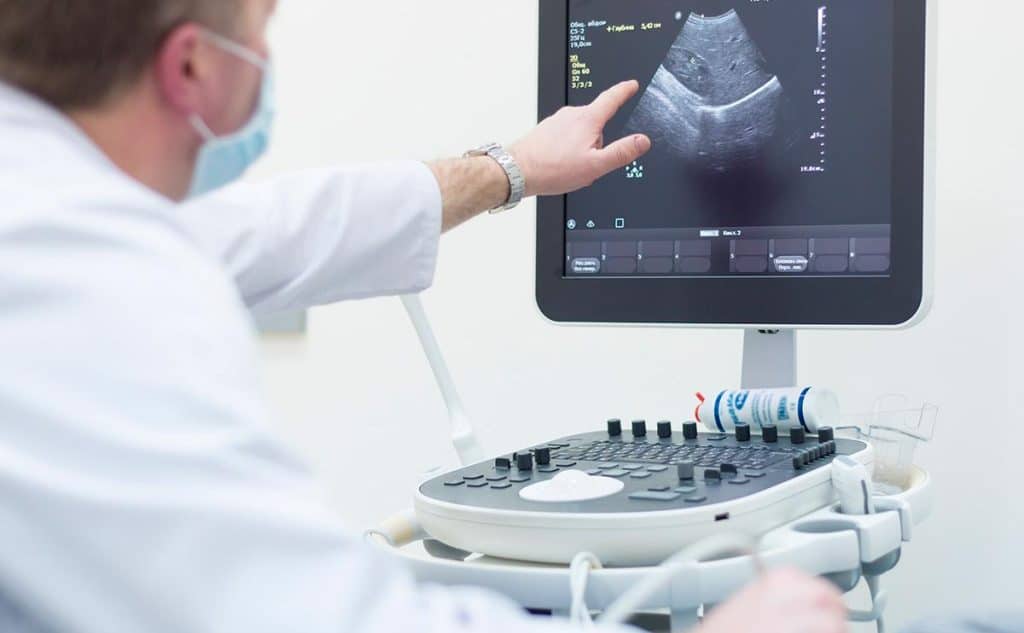
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, commonly associated with pregnancy monitoring, is a versatile imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of different parts of the body. It is particularly useful for early detection of cancer, heart diseases, internal medicine, vascular conditions, and a variety of other medical conditions.
Ultrasound can be used for other purposes and on various body areas, including breast ultrasound, pelvic ultrasound, vascular ultrasound, and musculoskeletal ultrasound. It is effective in detecting masses and types of abnormalities within the body. Ultrasound is an important diagnostic tool, often used complementarily alongside other medical imaging techniques.
How does ultrasound produce images?
- Ultrasound relies on the principle of sound wave reflection.
- A transducer sends high-frequency sound waves into the body, which bounce back from different tissues and return as echoes.
- The time it takes for these echoes to return is processed by a computer to create dynamic images.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a unique branch of radiology that focuses on the functional aspects of the body at the cellular level. Unlike other medical imaging techniques, it involves injecting radioactive materials known as radiopharmaceuticals, which are then tracked within the body. Nuclear medicine techniques, such as PET and SPECT scans, provide functional information about organs and tissues, making them powerful tools for diagnosing conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and thyroid disorders.
How do radiopharmaceuticals reveal cellular activity?
- Radiopharmaceuticals emit gamma rays, which can be detected by special cameras called gamma cameras.
- By monitoring the distribution of these radioactive substances,
- nuclear medicine specialists gain insights into cellular functions.
The Role of Radiology in Healthcare
Radiology plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare. It not only helps diagnose diseases but also guides surgical interventions, monitors treatment effectiveness, and assists in surgical procedures.
Radiologists work closely with doctors, surgeons, and other specialists to provide accurate diagnoses and clear treatment plans. Their expertise contributes to improving patient outcomes, making radiology an indispensable component of the medical field.
Applications of Radiology
Radiology is integral to diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions, from acute injuries to chronic diseases. Below are some key applications:
- Trauma and Emergency Care: X-rays and CT scans quickly identify fractures, internal injuries, and bleeding, enabling rapid treatment.
- Neurology: MRI and CT scans are used to diagnose brain tumors, strokes, and spinal cord abnormalities.
- Cardiology: Echocardiograms (ultrasound of the heart) assess heart function and detect heart conditions.
- Oncology: CT scans, MRI, and PET scans help detect, monitor, and assess tumor growth, evaluate treatment responses, and guide biopsy procedures.
- Obstetrics and Gynecology: Ultrasound monitors fetal development and identifies gynecological conditions like ovarian cysts and fibroids.
- Gastroenterology: Ultrasound and CT scans evaluate abdominal pain and detect conditions such as gallstones, liver disease, and pancreatitis.
Preparation for Radiological Exams
Preparation for radiological exams varies depending on the imaging technique used. For example, you may need to fast before a CT scan or fill your bladder for a pelvic ultrasound. The healthcare team will provide specific instructions to ensure accurate results. During the exam, you will be positioned appropriately, and the technician will operate the imaging equipment. It is essential to stay still to obtain clear images.
Benefits and Risks of Radiology
Radiology offers numerous benefits, including precise, non-invasive diagnostic capabilities that aid in the early detection and treatment of various conditions. However, it is important to be aware of potential risks, such as exposure to ionizing radiation in X-rays and CT scans. To minimize these risks and ensure patient safety, the healthcare team follows strict safety protocols.
HSI offers an opportunity for students interested in learning and studying medical imaging techniques and their applications. Through these training courses, participants gain both practical and theoretical knowledge to contribute to the advancement and development of this leading field.