In the modern medical world, ultrasound technology stands out as one of the most groundbreaking innovations, revolutionizing both diagnosis and treatment. What began as a pioneering method to visualize the human body has evolved into a versatile tool, utilized for everything from routine pregnancy monitoring to advanced therapeutic interventions. But what exactly is ultrasound? How does it work? And why is it considered a medical revolution? Let’s take a closer look at the world of this technology.
What Is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound refers to sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing, typically around 20,000 Hertz. In medicine, these waves are used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic ultrasound generates images of internal organs and tissues, while therapeutic ultrasound modifies or treats tissues.
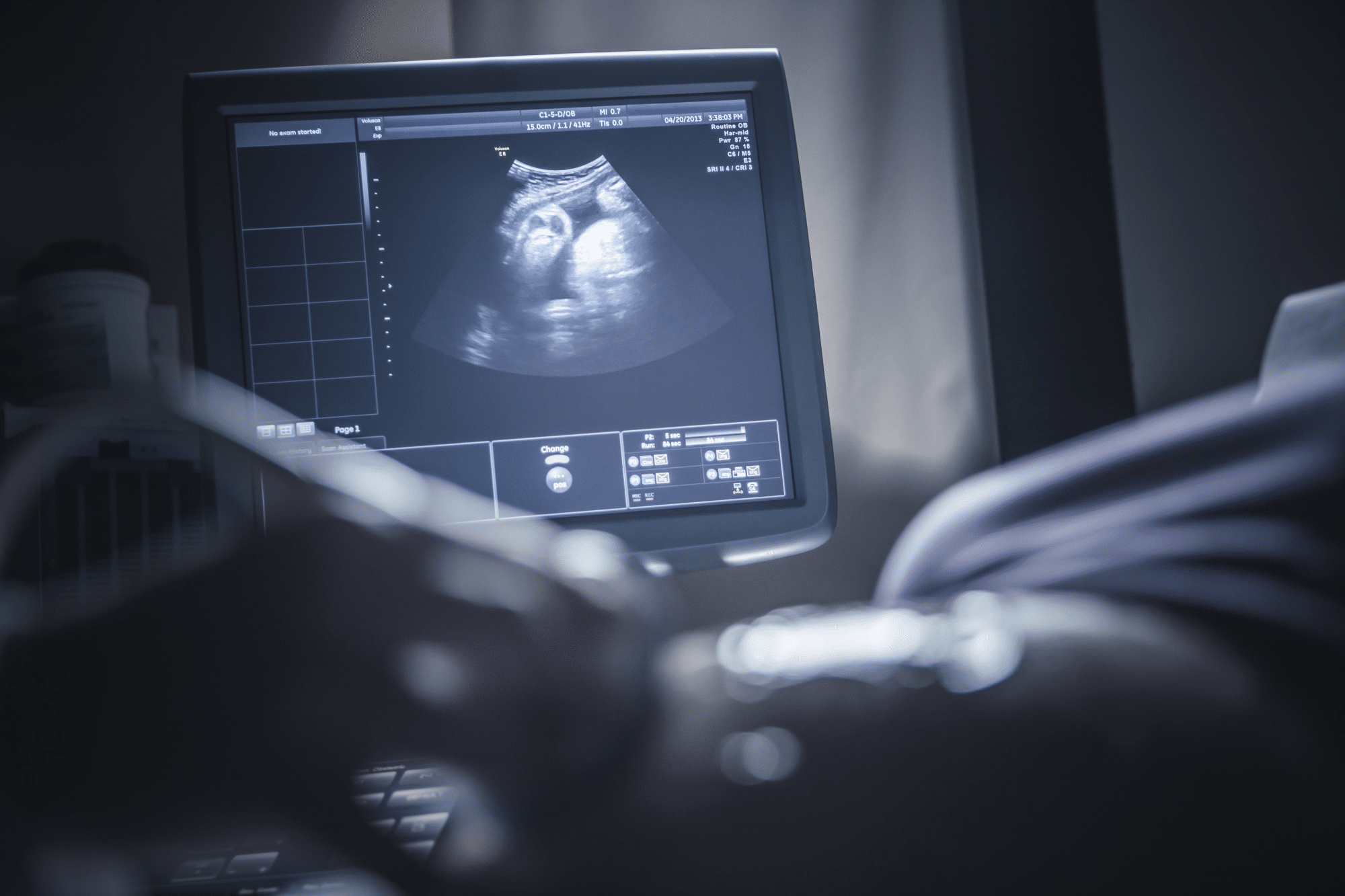
This technology is safe, non-invasive, and highly versatile, making it an ideal choice for various patient groups, including pregnant women and children. Unlike ionizing radiation, which can pose health risks if overused, it does not rely on ionizing radiation, thereby avoiding potential harm associated with its exposure.
How Does Ultrasound Work?
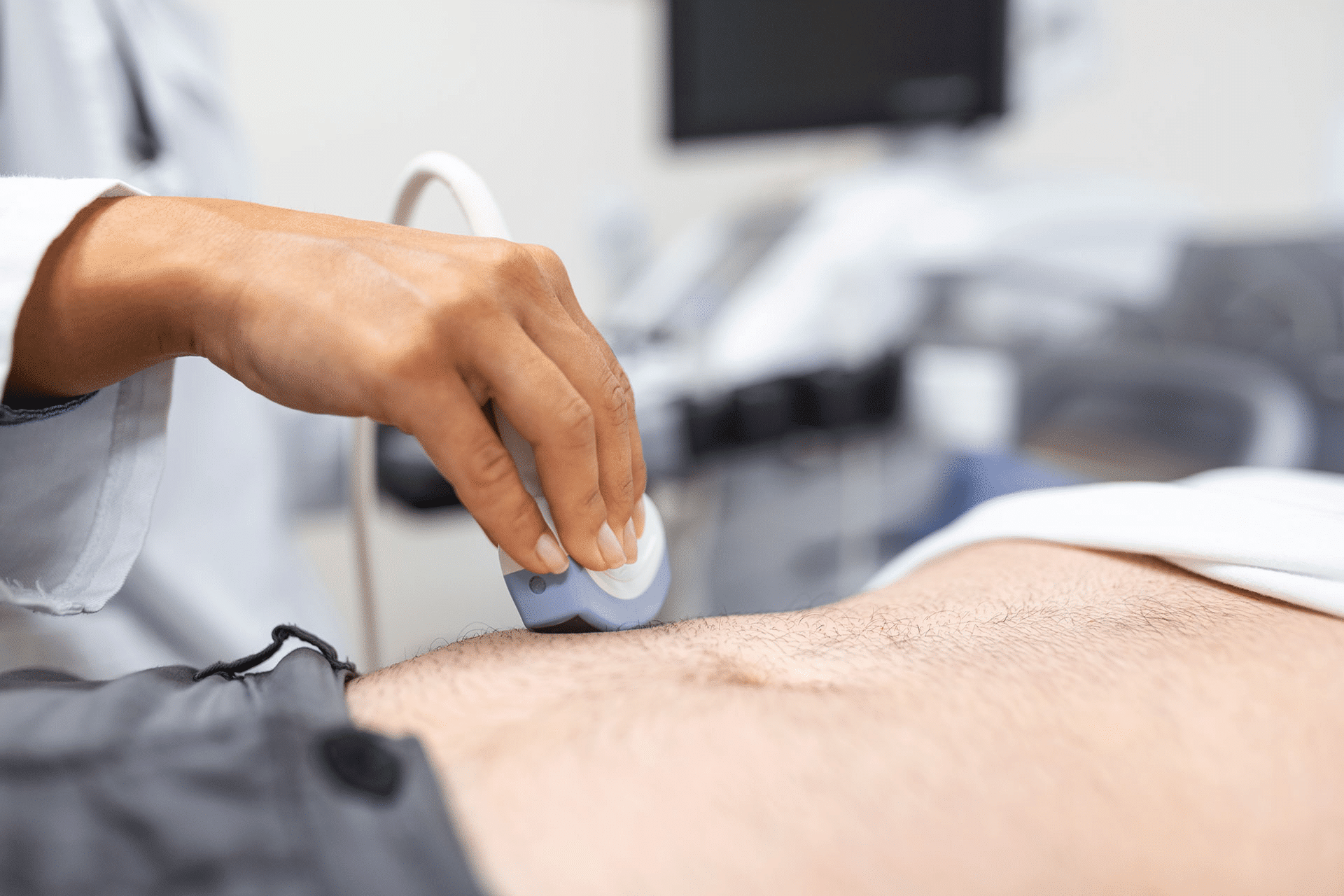
The technology relies on a device called a transducer, which emits and receives sound waves. The transducer contains piezoelectric crystals that produce sound waves when exposed to an electric current. These waves travel through the body, bouncing off internal structures and creating echoes. The transducer captures these echoes, which are then processed by sophisticated software to generate detailed images.
To ensure optimal results, a special gel is applied between the transducer and the patient’s skin. This gel eliminates air pockets that could obstruct the sound waves’ transmission, enabling accurate imaging. The technique’s precision allows for two-dimensional imaging of organs and tissues by analyzing the time and intensity of returning echoes.
Types of Ultrasounds
As a form of sound wave technology surpassing the human hearing range, ultrasounds have numerous applications thanks to its ability to penetrate tissues without causing harm. In medicine, two primary types of ultrasound are widely used: diagnostic and therapeutic. Let’s explore each in detail.
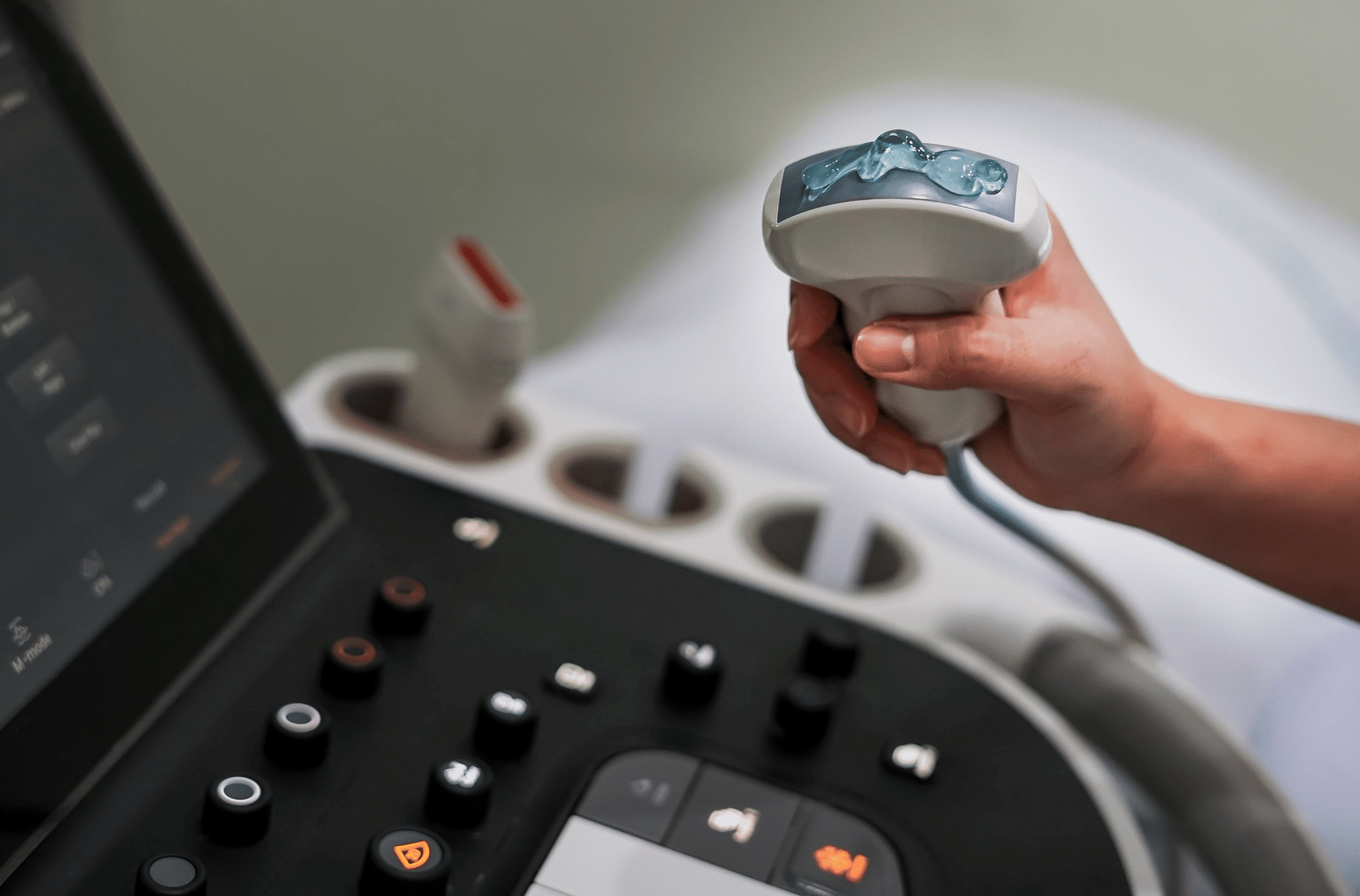

1) Diagnostic Ultrasound
Diagnostic ultrasound serves as the cornerstone of medical imaging. While often associated with pregnancy care—allowing parents a first glimpse of their baby—its applications extend far beyond obstetrics. It is used to image the heart, blood vessels, and various organs such as the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland.
One significant advancement in this field is functional, which combines anatomical imaging with tissue motion and blood flow analysis. For example, Doppler ultrasounds evaluate blood flow in arteries and veins, providing crucial insights into cardiovascular health. Similarly, elastography measures tissue stiffness, aiding in early detection of conditions such as tumors and liver fibrosis.
2) Therapeutic Ultrasound
Technology’s role isn’t confined to diagnostics; it’s also a powerful therapeutic tool. High-intensity focused ultrasounds (HIFU) is a prominent example, focusing sound waves on specific areas to destroy tumors, dissolve clots, or alleviate pain without invasive procedures.
Therapeutic ultrasounds also facilitates targeted drug delivery and accelerates wound healing. Its non-invasive nature reduces recovery time and minimizes potential complications, making it a valuable option for modern medical treatments.
This technology has undeniably transformed the medical landscape. With its diverse applications and safety advantages, it continues to be a cornerstone of innovation in healthcare, offering diagnostic clarity and therapeutic precision.
Innovations in This Technology
The field of this technology is witnessing continuous advancements driven by research and engineering. Among the latest innovations are wireless wearable devices that enable continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure. These devices represent a significant leap forward in telemedicine, allowing patients to receive high-quality care from the comfort of their homes.
Another notable innovation is the use of ultrasounds in precise surgical procedures. For instance, technologies like ultrasound-guided biopsies allow doctors to accurately target suspicious tissues, reducing the need for exploratory surgeries.
What Are the Everyday Applications of Ultrasound?
Ultrasound has found its way into nearly every medical specialty. In cardiology, it is used to evaluate heart function and detect conditions such as valve disorders or fluid accumulation around the heart. In emergency medicine, it is utilized to assess internal injuries or bleeding, making it an indispensable tool in critical situations.
In musculoskeletal medicine, ultrasound helps diagnose conditions like tendon tears and joint inflammations. It is also used in dermatology to evaluate skin layers and in ophthalmology to measure internal structures of the eye.
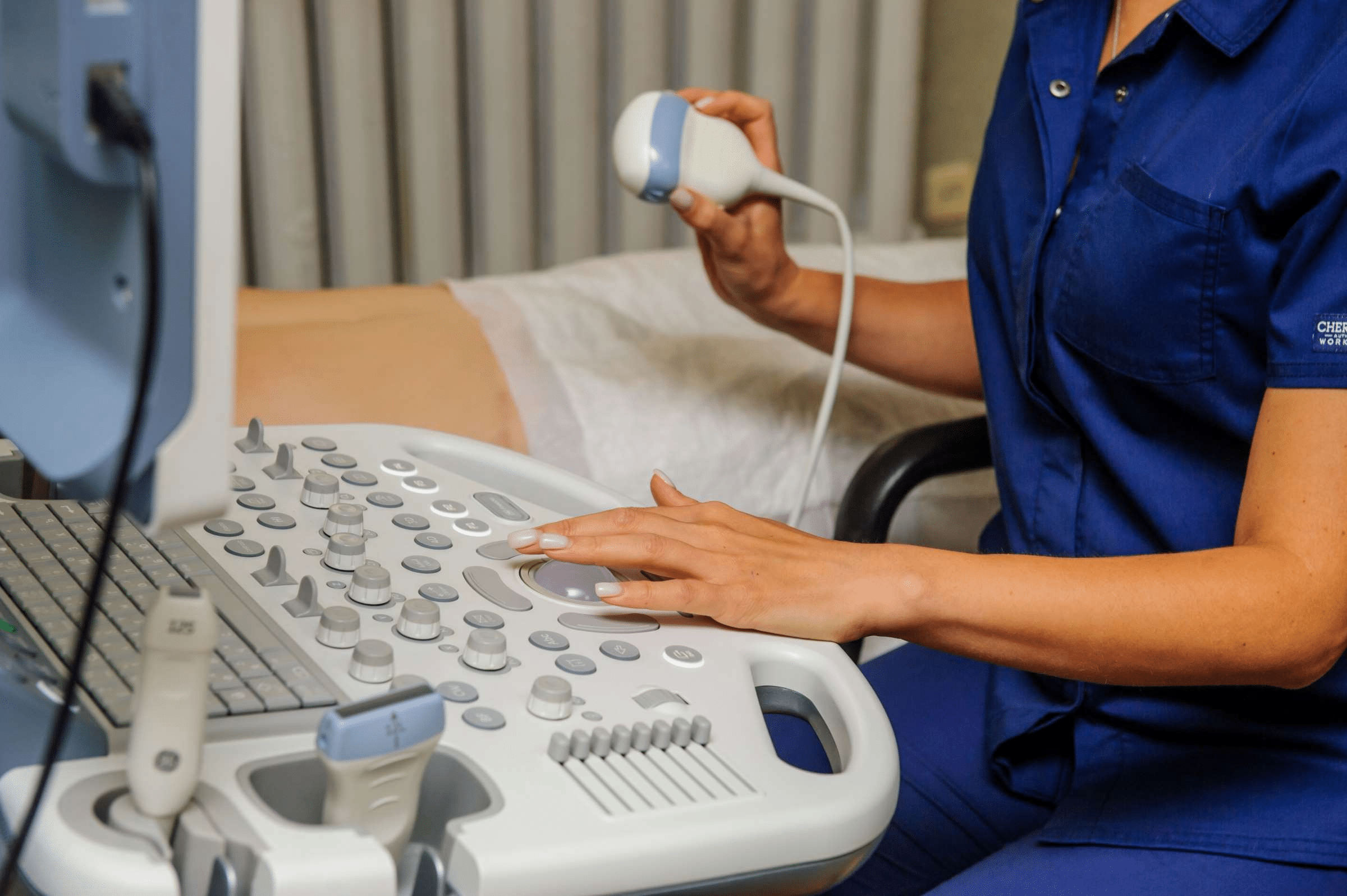

Addressing Safety Concerns of Ultrasound
Although it is considered safe, it must be used with care. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established strict guidelines to ensure devices operate within safe limits. However, it is recommended not to use this technology for non-medical purposes, such as creating souvenir videos during pregnancy. it should only be used when there is a genuine medical need.
The Future of Ultrasound: What Lies Ahead?
The future of this technology holds immense potential. Researchers are exploring its applications in 3D bioprinting, where it is used to shape special inks within tissues to repair bones or soft tissues.
Scientists are also investigating its potential to induce hibernation-like states in patients by targeting specific brain regions. They have successfully reduced metabolic rates in animal models, paving the way for possible applications in critical care.
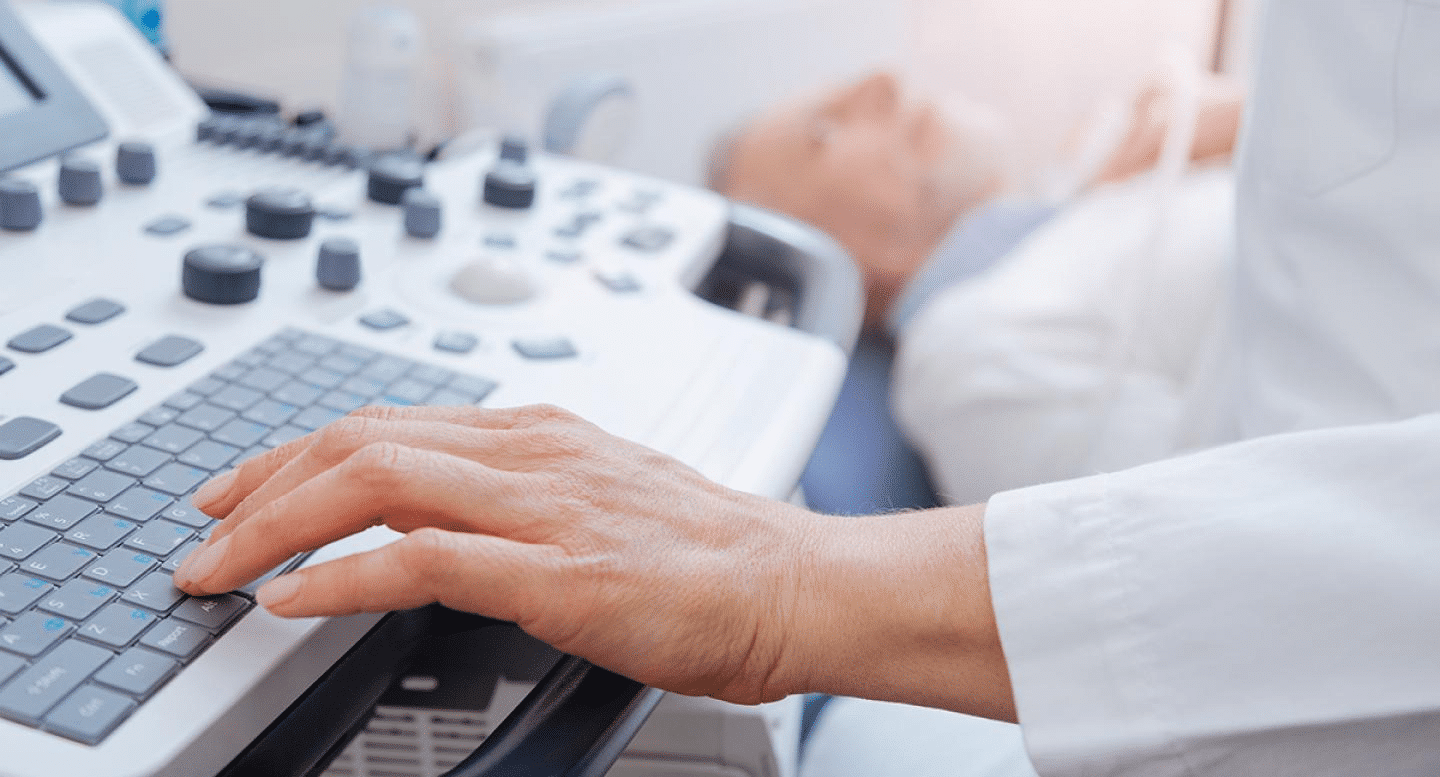

Why Does Ultrasound Matter?
Ultrasound is a cornerstone of modern medicine due to its accessibility, affordability, and versatility. Unlike many other imaging technologies, it is portable and does not require complex infrastructure, making it invaluable in rural and underserved areas.
Additionally, it provides real-time imaging, enabling rapid decision-making in critical situations. Whether guiding surgeons during procedures or monitoring a fetus’s heartbeat, it continues to save lives and improve quality of life.
In conclusion, the technology represents a significant advancement in the medical field, enabling safer and more effective diagnosis and treatment. If you work in healthcare and aim to enhance your skills and knowledge in this area, HSI offers the perfect solutions.
Through comprehensive training programs in healthcare, you can learn modern strategies and techniques to enhance your practical skills in applying this technology and other medical innovations. HSI also provides consulting and mentorship programs for professionals, fostering career development and offering innovative solutions to improve patient care and operational efficiency.
Source: Ultrasounds – National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering